Waste Heat Recovery
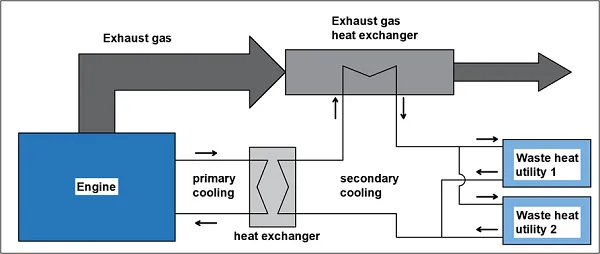
Waste heat recovery entails capturing and reusing the waste heat in industrial processes and delivering it to a device or process where it can be used as an effective, economical and environmentally friendly way to save energy. Usually, hot waste-gas losses are a current issue of operating boilers, furnaces, kilns, ovens or dryers. Hot waste-waters appear in many industrial systems, as well reducing these losses through recovery presents a significant opportunity to improve the overall energy efficiency.
Stage of Life Cycle
Non Product output
GHG Reduction Potential
GHG reduction potential varies according to the type of technology (e.g. regenerator, recuperator, economizer), the equipment, the processes configuration, the source of waste heat (e.g. process exhaust) as well as other technical aspects. Such as thermal recovery capability or chemical/physical constraints of materials used in heat recovery mechanisms or end use for recovery heat (e.g. boiler feedwater, combustion). According to estimates by the U.S. Department of Energy under the Industrial Technologies program, about 20 to 50% of the energy consumed in manufacturing processes in the chemical industry is ultimately lost through waste heat contained in hot exhaust and liquid streams, as well as heat conduction, convection, and radiation from hot equipment surfaces and from heated product streams. In some cases, such as industrial furnaces, efficiency gains through heat recovery can improve energy efficiency by 10% to 50%. Example: A chemical A is produced in an endothermal process, and the heat required is hot water generated in a fossil fueled boiler. The production of another chemical B requires a cooling as the reaction is exothermal. Instead of releasing the heated-up coolant into to the ambient, it can be used to provide heat for the endothermal reaction in case of chemical A. Hence, emission are siginifcantly reduced, as fossil energy inputs are substitued directly with emission-free reused waste heat.
Solution Maturity Status
Under development:
This technology has been operating for a number of years and is well-known/ successful in its industry or market.
Identification Keys / Drivers & Barriers
Infographic